The Impact of Biotechnology on Animals
a journey through the lives of animals and how they benefit humans...
Further Research
Part of the Naticonal Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed is a search engine acessing the MEDLINE database for topics asscoiated with life sciences. The site provides unbiased and brief information on the current issues involving animal biotechnology
The UCDavis website provides an interview with Jerrold Tannenbaum referred to as the, " only professor of veterinary ethics and law in the world". He answers common questions about animal-rights activism and explains his reasoning behind animal experimentation
Funded by Public Health Service, OLAW is responsible for the care and regulations involving laboratory animals. It works to ensure the proper and humane care involving PHS funded research. It descriptively explains the ethical guidlines and regulations it follows for the protection of the laboratory animals.

The organization is responsible for funding most of the research involved with animals. The site works as a database and provides information from other sites such as the Animal Welfare Institute and Institue for Animal Research. Bibliography, animal guidlines, and databases on alternative methods can all be found with detailed information.
Listen to various discussion by professionals on the ethics of animal experimentation and the imapact of such research in the future
Media
CITATION 2
Dr. Oppenlander explains here how ethical considerations in eating meat goes beyond animal rights.
CITATION 3
The brief video explores the relationship between the health of animal and that of food safety. Explains how altering the way animals are raised and kept, could ultimately affect the consumers of animals and animal products
I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. I’m a great place for you to tell a story and let your users know a little more about you.
Ethical and social issues involving animal biotechnology are of significant importance because they determine the future market success of animal products. Questions regarding animal welfare, food safety, enviornmental concerns,and labeling food products arise whenever a new technology or technique is introduced. Researchers face constant disapproval when they are unsuccessful in persuading others of the motives behind their projects. The public concerns can be explained via three broad categories
-
the impact of the technology on the animals themselves
-
the regulations and procedures involved with the agrifood system
-
the impact of the technology on humans
Ethics and social issues of animal biotechnology
Animal Welfare
Animal Welfare is defined as,"how an animal is coping with the conditions in which it lives". According to the Veterinary Medical Association, animal welfare includes proper consideration of nutrition,disease prevention and veterinary treatment, appropriate shelter, management, humane handling and humane slaughter. The association highlights that animal welfare is influnced by a person's morals and values, and is not limited to health, productivity, behavior, and physiological responses. Although the majority of the experimentation and research conducted by various organizations concern the health of the animals; such as being disease resistant, the public is not satisfied. Opposers argue that despite the motives of agriculturalists, the animals' pain is inherent as they are encaged in sterile labs and are forced to suffer diseases and injury.Oppositionists further argue that cloned animals rarely succeed in outliving their life expectancy, and tend to suffer from abnormally large organs that lead to resperitory failures, low-blood sugar and weak immune systems. Many believe that animals are forced to endure the same "inhumane" experiments, regardless of the countless amount of failures. Religion plays an essential role in animal biotechnology. Many people believe that the techniques of animal biotechnology are unnatural as it involves altering the natural world. Transgenic animals also pose problems for vegetarians/vegans. If, for example, an animal gene is introduced into a fruit, would the fruit be considered a type of "meat"? Such questions need to be answered before companies can market products that involve genetic techniques.
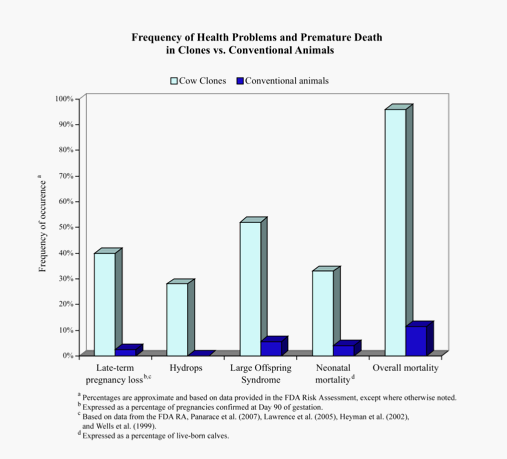
This graph displays the diseases that cloned animals experience vs the amount that naturally produced animals experience. The results show that cloned animals experience many more obstacles in their lives compared to other animals.
NOTE: the survery is shown by the endcloning.org, a site geared toward eradicating cloning. The survey is said to be a compilation of surveys conducted by the FDA, RA, and related organizations. FIND MORE INFORMATION:
The health of the human population depends on the safety of the food supply. Even though animal biotechnology has the capability to enhance many characteristics of food products, it is not a method that is accepted by many people. The public fears that adding additional hormones in the animal may affect the person who consumes that animal. From swine flu to the mad-cow disease, there are several diseases that animals can transmit, and scientist are not fully aware of the pathogen involved.The National Academies of Science (NAS), however, has recently released a report titled Animal Biotechnology: Science-Based Concerns that assured everyone that the overall concern level for the food safety was relatively low. Furthermore, the nutritional content of the animal does not change and is not harmful to consume.
Food Safety
Because altering the enviornment can ultimately affect the entire food chain, the introduction of transgenic animals may pose a threat to the fragile ecological balance. The trangenic population have the capability to reproduce, and therefore, can establish themselves as persistent species. This permanent establishment may severely damage the ecosystem. Despite intense study of the phenotypes of certain species, scientist cannot completley guarantee the result of transgenisis on the host animal. Livestolk, however, pose the least risk to the enviornment as they are much larger compared to other animals, and can easily be maintained by agriculturalists. While water organism, such as fish are much more difficult to control once released to occupy the wild. The introduction of a new animal may affect the success of other animals as well. Such possibilities must first be eradicated or limited, before they animals can be allowed to reproduce freely, in the wild.
CITATION 4
Enviornment
Regulators/Labeling
Currently, there has been no regulations or laws that have been enforced to deal with animal biotechnology. The main governing body for the techniques is the FDA and USDA. The FDA is responsible for the regulation of drugs, vaccines, certain foods, and biological devices. The agency faces many criticisms on its regulation of livestock as its primary purpose is to regulate drugs. Ths USDA is an executive department responsible for promoting agriculture trade and production, as well as food safety. Animals that are engineered for specific purposes such as pigs, are regulated by the agency
Another one of the biggest controversies in animal biotechnology involves the labeling of the products produced by genetically engineered animals. Opposers believe that if a process has been proven safe by the FDA, then it is "unfair" to require a product to be labeled, merely because of the process it was made from. Meanwhile, supporters argue the "right-to know" point. They state they have the right to know as consumers, so they can make choices according to their personal ethics.
The Future
While envisioning the future of animal biotechnology is difficult, there are some things that can be said with confidence. The regulating agency, FDA, will establish policies for the commercial uses of products created through the technology. If the FDA approves the genetically enginnered products for human consumption, there will be many companies that will be able to market milk and meat from cloned animals. Additional benefits may include:
-
research in cell particles; an alternative to full organisms
-
vaccinology
-
animal models for various diseases
-
transgenic animals
-
cloning of endagered species
Need Help?
Important Notes:
When browsing this website, keep in mind that each information is cited for a reason. Citations will include links to alternate websites from where the information has been collected. Videos are included for those who prefer a visual aid. Each page will have a related links bar, where innovators and related organizations have been highlighted. There is also an RSS Feed that will automatically feed information related to animal agriculture. Click on forward and backward to navigate between the pages




